A Snapshot of the U.S. Wind Industry
At a recent Capitol Hill hearing I was surprised to learn that it was far from common knowledge just how competitive wind power has become. As a result, a bit of a data and price update memo may be of use, even to those who follow the industry. In addition, I will summarize the data on a few of the least cost wind farms in the nation.
Representative Wind Project and Wind Power Costs
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) recently examined the estimated installation and power costs for twelve recent wind projects, finding that 2007 wholesale power prices for these projects range from 2.5 cents/kWh to 6.4 cents/kWh. Six of the projects provide wholesale power at less than 3 cents/kWh. These prices reflect available state and federal incentives, such as the Production Tax Credit, and any value from Renewable Energy Credits.
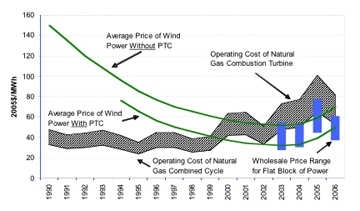
As shown in Figure 1, also developed by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, average wind power prices have trended downward over time, notwithstanding a more recent increase in those prices. Even with the increase, however, wind power is found to be competitive with wholesale power prices and with the cost of operating new natural-gas power plants. This is especially true if the production tax credit is maintained.
Factors Affecting Costs and Future Cost Trends
As the LBNL findings show, the cost of wind projects can vary by a factor
of three or more. The reasons for these are varied but include:
installation and material costs (turbines purchased in 2004 and 2005 are
less expensive than those purchased in 2006 and 2007), relative wind
resources (Class 5 wind sites result in higher capacity factors than Class
4 or 3 wind sites), and developer/owner (i.e. experienced developers such
as FPL Energy may
be able to develop and construct projects at lower cost).
Wind power prices have trended up over the last couple years as shown in
Figure 1, and as confirmed by Figure 2, a reflection of increasing
installed project costs. This trend is now seen across all
capital-intensive energy technologies. Reasons for these increasing costs
include: weakness in the dollar; rising materials costs; the move towards
increased manufacturing profitability; and a shortage of manufacturing
components.
Although many of these cost drivers are global, higher costs for wind in
the U.S. are also attributable to limited U.S.-based manufacturing of
wind-turbines. U.S. turbine manufacturing remains somewhat limited due to
uncertainty about demand and the continuation of the Production Tax
Credit. New manufacturing plants are being built in the U.S. (for example,
the Clipper Windpower plant in Iowa and the Suzlon plant in Minnesota),
albeit not at the same pace as in other parts of the world. Some of the
2006 wind power prices reflect lower turbine costs locked in 18-24 months
earlier.
In 2007, wind project and power costs are likely to trend higher as they
will reflect increasing turbine costs. The increasing cost of wind
turbines is partially mitigated by improvements in wind project
performance. Increases in project capacity factors have been primarily
driven by higher turbine heights, improved siting and technological
advancements. As noted earlier, however, these cost trends are affecting
other forms of electricity generation as well and, as Figure 1 shows, wind
power remains competitive with wholesale power prices and with the cost of
operating new natural-gas power plants.
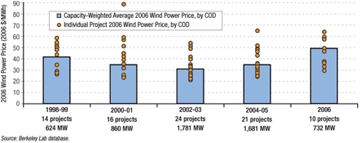
2006 Wind Power Price by Commercial Operation Date (COD)
Global Wind Energy Costs
The U.S. has the third-largest cumulative wind capacity globally, lagging
only behind Germany and Spain. Both Germany and Spain have more sizeable
national support programs for wind energy (such as guaranteed feed-in
tariffs) as compared to the U.S. In Germany, grid operators must pay wind
energy providers .0836 €/kWh (.12 US$/kWh ) for turbines installed in 2006
for at least the first five years of operation. This starting tariff
decreases by 2 percent annually.
In recognition of increasing turbine costs, Germany recently reduced the
annual tariff degression from 2 percent to 1 percent per year. Germany
will also pay a bonus of € 0.007/kWh (.01 US$/kWh) for wind turbines that
are more compatible with the needs of the grid. Germany manufacturers
report explosive job growth for the wind energy sector and the creation
and influx of technology firms to support the wind energy industry. All
told, job growth in the roughly 25 percent of the German energy sector
devoted to renewable energy was in 2006 equal to job growth in the entire
rest of the energy generation sector.
As cumulative wind capacity increases in Germany and Spain, both countries
are revising their rules regarding price support for wind energy. Spain
has draft rules to establish maximum, as well as minimum, prices to be
paid to wind farm operators. Under Spain's draft rules, for the first five
years of operation, a wind farm operator will receive a maximum of .084
€/kWh (.12 US$/kWh) and minimum of .068 €/kWh (.099 US$/kWh). The tariff
levels decline over the duration of the plant's operation.
Both Germany and Spain, as well as Denmark and other nations that have
supported the development of significant wind energy industries, have
documented significant job growth in the clean energy sector. Export
orders for wind turbines in Germany, Spain and Denmark have now resulted
in significant new job creation.
Green-Biz Editor-at-Large Daniel M. Kammen is the Class of 1935
Distinguished Professor of Energy at the University of California. He
co-directs the
Berkeley Institute of the Environment and is founding
director of the
Renewable and Appropriate Energy Laboratory. Kammen has
served as a lead author for the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change,
which shared the 2007 Nobel Peace Prize. He has appointments in the Energy
and Resources Group and the Goldman School of Public Policy.
This article was reprinted with permission from Greenbiz.com.