Location: New York
Author: Cheng & Valerie Mercer-Blackman
Date: Wednesday, November 7, 2007
* Average petroleum spot price hit record highs in early November
* Triggered by geopolitical risks, bad weather in Gulf of Mexico, tightening market conditions, and weaker dollar
* Hike may boost headline inflation but impact on growth likely to be marginal
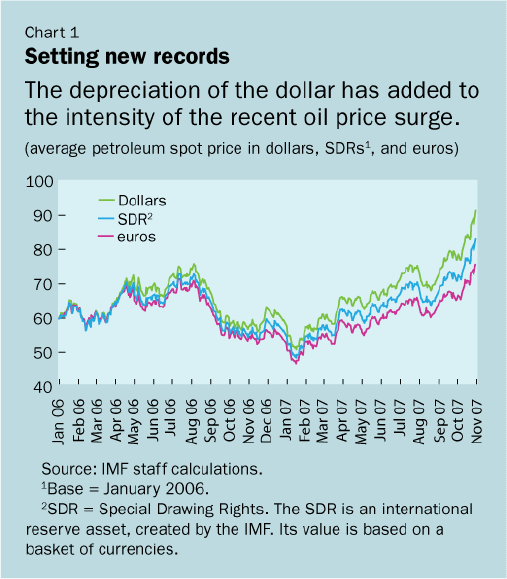
With prices nudging record highs, the recent oil spike has received a lot of media attention.
On November 2, the average petroleum spot price (APSP) set a new high, closing at over $91. The three main benchmark prices for oil also reached record highs during the same week, with West Texas Intermediate closing at almost $96, Brent at more than $92, and Dubai at more than $85. Measured in euro and SDR terms, however, the surge has not been as stark, reflecting the depreciation of the dollar (see Chart 1).
As of early November, futures and options markets indicate that the APSP
will average over $87 per barrel in the fourth quarter of 2007 and over $86
per barrel in 2008, with a more than one in four chance that Brent crude
prices could be above $100 by early 2008.
The recent oil price surge was sparked by heightened geopolitical concerns
about growing tensions along Iraq's border with Turkey, continued concerns
about Iran, and bad weather in the Gulf of Mexico. Increasingly tight oil
market conditions also played a role, as did the weakening dollar, according
to analysts at the IMF.
Oil demand growth is expected to remain robust throughout the rest of 2007,
supported by strong growth in emerging markets, particularly China and the
Middle East (see Chart 2).
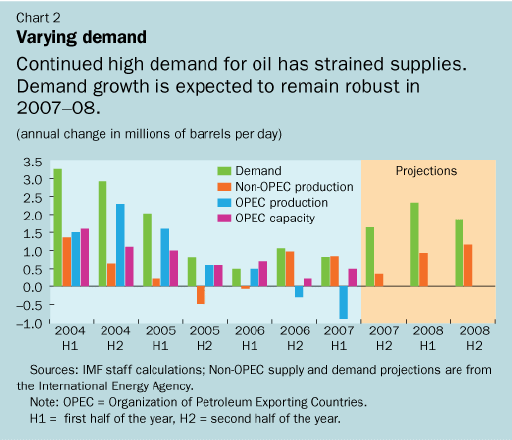
But supply has lagged behind and inventories are falling. During the first
nine months of 2007, world oil supply declined moderately by 0.1 millions of
barrels per day (year on year), reflecting a decline in the output of the
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and limited output
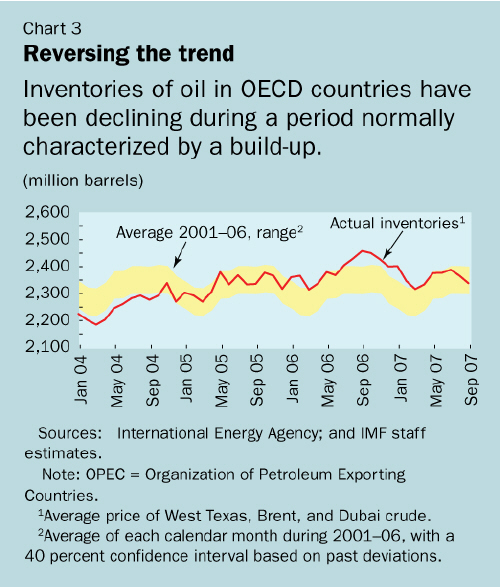
growth in oil-producing countries that are not members of OPEC. As a result,
commercial inventories in OECD countries fell in the third quarter, a period
normally marked by inventory accumulation (see Chart 3).
Supply is unlikely to catch up with demand growth because of the increasing
technological and economic challenges for oil production. As a result, tight
market conditions are expected to persist and possibly intensify, assuming
strong GDP growth continues in emerging markets.
The oil price surge is not an isolated event. Many other
commodities—including precious metals, industrial metals such as lead and
nickel, and foods such as wheat and edible oils—have all set record highs
during 2007. Indeed, the dollar depreciation has amplified the oil price
surge in dollar terms. While the APSP rose by almost 55 percent in dollar
terms during the year ending October 2007, it rose only by about 36 percent
in euro terms.
Apart from this "accounting effect," some market analysts suggest that the
weakening of the dollar, combined with the financial turbulence linked to
the subprime mortgage market in the United States, may have induced
investors to diversify away from dollar-denominated financial assets toward
commodities as "alternative assets."
Rising oil prices will likely boost headline inflation in the months ahead,
but only slightly. The direct effect of the recent oil price rise on
headline consumer price index (CPI) inflation in the United States is
estimated to be about 0.1 percentage points by the end of the year. Overall,
the impact should be manageable, because greater monetary policy credibility
has anchored inflation expectations more securely, particularly in advanced
economies, according to an IMF analysis. The situation may be more
challenging in some emerging market and developing countries where
overheating pressures are of greater concern and rising fuel costs may put
pressure on household budgets and external balances, particularly in
low-income oil-importing countries.
The impact on global economic activity should also be limited. First, the
depreciation of the dollar has softened the impact of the oil price surge on
other major consuming countries. Second, the price rise has been driven by
sustained strong demand growth rather than supply shortfalls. Third,
compared with the oil price surge in the late 1970s, economies today are
much less energy intensive. Fourth, in the case of the United States, the
low season of gasoline consumption during September-October has so far kept
retail gasoline prices comfortably below the highs set in May 2006.
That said, a supply-driven spike to oil prices caused by a serious
deterioration of security conditions in the Middle East could have a
significant impact on global growth. The April 2007 World Economic Report
simulated the impact of a supply-induced oil price hike using the IMF's
"Global Economy Model."
The findings suggested that a sharp supply-induced rise in oil prices could
result in a global slowdown, as income is redistributed to oil-exporting
economies, which have a lower propensity to spend than oil-importing
economies. Higher oil prices would also raise the cost of production and put
upward pressure on the aggregate price level. This would cause central banks
to increase interest rates. Together with the direct impact on production
costs, higher interest rates would then further dent economic activity in
the short run.

To subscribe or visit go to: http://www.riskcenter.com