Indigenous tribes, ranchers team to battle Amazon fires
Facing the worst outbreak of forest fires in three years, cattle ranchers and indigenous tribesmen in the southern Amazon have teamed up to extinguish nearly two dozen blazes over the past three months, offering hope that new alliances between long-time adversaries could help keep deforestation rates in the Brazilian Amazon on a downward trajectory.
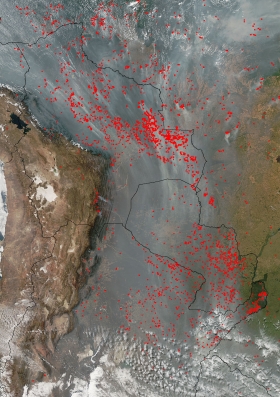
The voluntary fire brigades, which have now spent more than 400 hours battling fires, are the product of partnership between Aliança da Terra, a Brazilian nonprofit working to improve land stewardship by cattle ranchers in the heart of the Amazon; Kayapó and Xavante Indians; local authorities; and the U.S. Forest Service. Over the past two years the Forest Service, with financial assistance from USAID, has led three intensive training sessions on tactics for fighting wild fires. The training came at an opportune time: the number of fires burning in the state of Mato Grosso surged from 5,000 last year to 18,800 this year, the highest since 2007. Exceptionally dry conditions have exacerbated fires set annually for land-clearing. An image released two weeks by NASA shows smoke obscuring a 2,500-kilometer corridor extending from Peru, Bolivia, and Brazil in the north to Argentina in the south. 148,946 fires were burning at the moment the photo was taken.
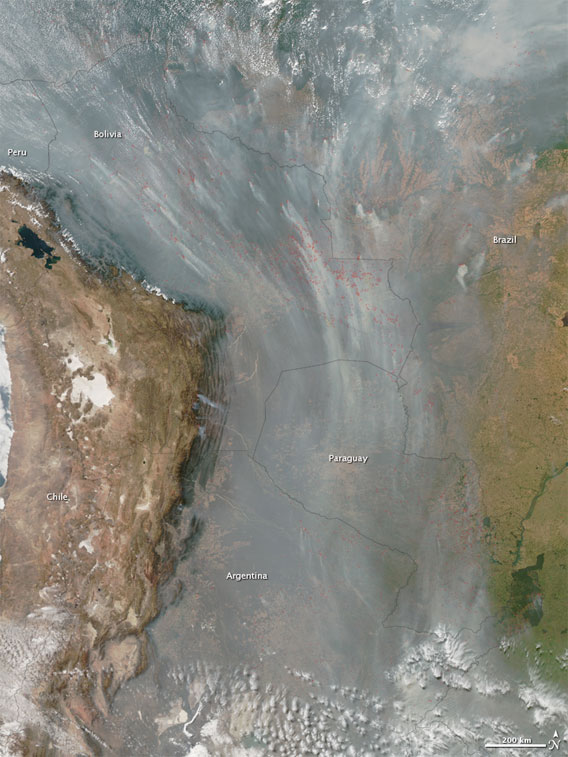
NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. Click image to enlarge.
Fire has long been used in the southern Amazon as a way to establish land claims and prepare pasture for low-intensity cattle grazing. But as some ranchers have improved their management practices and in the process, boosted the productivity of their holdings, fire has become an enemy.
 Indigenous volunteer firefighter in Mato Grosso.  Indigenous firefighters and smokejumpers from the United States Forest Service.  Indigenous firefighting team in Mato Grosso.  Alianca's firefighting team in Mato Grosso.  Pasture fire burning behind Alianca's firefighting truck.  John Carter.  The teams, together with USFS smokejumpers.  Firefighters in training.   Images courtesy of USAID |
But John Cain Carter, the U.S.-born rancher who founded and runs Aliança da Terra, says this has changed. Ranchers are now concerned about losing their investment in maintaining productive pasture. Loss of quality pasture now can leave cattle without fodder until January. In the meantime, cattle will starve without supplemental feed from another source, a costly course of action for an already marginal business. Fire further damages fencing and can wipe out the gardens and farms of small landholders.
Fire also puts forest reserves at risk. Under Brazilian law, landowners are required to maintain 80 percent forest cover on their holdings. Fire—which can spread easily from adjacent pasture lands, especially in years like this one where no rain has fallen since late April—can leave a rancher liable for hefty fines, if local authorities choose to enforce the law.
Once forest is ignited, it extremely difficult to extinguish. Carter says the fire-fighting crews organized by IBAMA, Brazil's environmental enforcement agency, have often abandoned fires once they have spread into forest areas. The Forest Service-trained brigades on the other hand have fought—and doused—several fires burning in dense forest, include conflagrations said by IBAMA to be "impossible to extinguish."
All told, Aliança da Terra's brigade has put out all 22 fires it has faced in pasture, cerrado grasslands, and forest.
The efforts have been assisted by the availability of gear and strategically-placed water tanks funded by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, a major backer of Aliança da Terra. Several ranchers have also provided gear and financial support. One even contributed a truck.
"This firefighter brigade is now seen as heroes by the farmers, the local population, the squatters and the Indians," said Aliança da Terra's Carvalho. "The brigade controlled the fire that would otherwise still be burning."
Edimar Santos Abreu, a former "squatter" or illegal settler, who now heads up Aliança da Terra's brigade, said the success in fighting fires marks an important change in the region, where squatters, Indians, ranchers, soy farmers, and land speculators have long been at odds, with conflicts often ending in bloodshed.
"We are all in the fight together," he told mongabay.com in Portuguese.
The benefits of working together to fight fires extend well beyond protecting against financial losses. Hospitals in the region are presently fully of patients with respiratory problems caused by breathing the choking smoke. Reducing fires will reduce health costs.
The smoke also makes transportation hazardous.
"You don't want to be in this part of Mato Grosso right now. The smoke is so thick, it's hard to breathe and dangerous to fly," said Carter, noting that smoke is less bad in areas where the fire brigades are active.
The success in extinguishing fires also raises an interesting prospect—the emergence of an informal system of governance in region where law enforcement is virtually unknown.
Frank Merry, a scientist at the Moore Foundation, says this development could be the most important outcome of the fire-fighting effort.
"A co-benefit is not only fighting the fires—which, of course, is huge since fire is one of biggest threats to Xingu National Park—but the establishment of frontier governance," he told mongabay.com. "Having the cowboys and Indians work together sows the seeds of governance and suggests a breaking down of some of the cultural barriers between the frontier groups who have been traditional enemies."
"To me this is a really interesting entrance to frontier governance outside rule of law," he continued. "It is a form of self-generated governance."
The brigade system is set to expand to 16 counties, including five surrounding the Xingu National Park—Gaúcha do Norte, Querência, São Felix do Araguaia, São Jose do Xingu, and Santa Cruz do Xingu—which have nearly 13 million hectares of tropical forests. Members of the current brigades will become trainers of tribes and private landholders once the dry season ends. Aliança da Terra will train "non-Indian" groups, while Colonel Mariano of Mato Grosso's Corpo de Bombeiros will coordinate indigenous training. Both groups will work in tandem: Indians helping out on private property as well as in the park and the ranchers, farmers, and settlers doing the same. All groups will be connected by radio, according to Carter, who says the program may be adopted state-wide.
 Click to enlarge |
Carter believes the fire-fighting effort could help increase participation in Aliança da Terra's cadastro or land registry system, which it hopes will eventually create a path for ranchers to sell certified 'deforestation-free' beef at a premium or qualify for other benefits, like cheaper loans or better access to markets. To be a member of Alianca's system, a landowner must meet certain criteria including reporting and monitoring requirements; implementing "no burn" management practices; protecting riparian zones; maintaining forest reserves as specified, but usually unforced, under Brazilian law; and establishing a 10-m wide fire guard between forest and pasture to prevent fires from "escaping" into forest areas. These measures could someday help transform the Brazilian cattle industry from one of the biggest drivers of deforestation to a key partner in saving the Amazon.
Copyright mongabay 2010 To subscribe or visit go to: http://news.mongabay.com