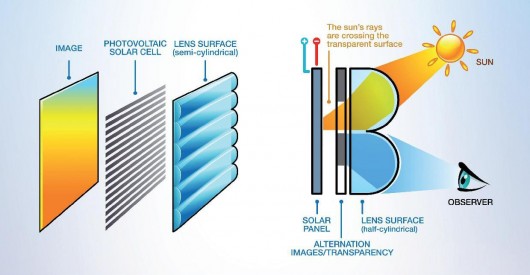
Wafer thin and flexible - Wysips film technology allows light to pass through a semi-cylindrical lens onto thin strips of photovoltaic cells below, while also allowing the surface underneath to show through
Mobile phones sporting photovoltaic panels are nothing new but thanks to some lens wizardry, a French company recently showed off a prototype phone where the touchscreen display itself housed the solar-soaking cells. Similar to the lenticular optics which sends slightly different images to each eye for glasses-free 3D viewing, Wysips technology allows light to pass through a semi-cylindrical lens onto thin strips of photovoltaic cells below, while also allowing the surface underneath to show through. The developers say that many surfaces could potentially become self-sufficient power producers.
The idea for Wysips is said to have been inspired by the holographic process used on book covers, where the image changes depending on the viewing angle. "What if I used these lenses to concentrate light onto thin strips of photovoltaic material located between the image strips?" optics enthusiast Joël Gilbert asked himself. "From one angle we'd see the image and from another, the solar panel."
From there, a flexible lenticular film was developed onto which micron-sized photovoltaic strips were deposited. Viewed from certain angles, it appears transparent, but light hitting at just the right point results in energy production – both indoors and outside. The company says that its technology ranges in thickness from 0.1 to 0.5 mm and is about 10 percent efficient – which isn't too far from recent developments from the likes of Honda Soltec, and given the scope of potential applications, it's quite a marvel.
The French technology company has chosen to concentrate its initial development efforts on applications like mobile phones, LCD screens, digital tablets, technical textiles, outdoor displays and so on. The kind of power generated by the prototype mobile phone on show at CTIA 2011 probably won't be enough to make a smartphone completely battery-free, but should help to significantly extend the device's use before needing to be plugged into the mains for a top-up. The Wysips film would also sit below the capacitive surface, so shouldn't interfere with that glorious multi-touch interactivity we've all come to rely on.
This is an interesting development, full to bursting with potential. With Wysips currently looking for manufacturers ready to use its technology, it probably won't be too long before we see the first commercial examples hitting the shelves.
Copyright © gizmag 2003 - 2010 To subscribe or visit go to: http://www.gizmag.com