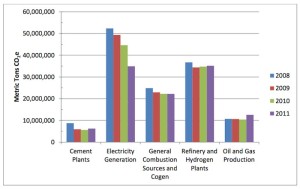
Californiaís CO2 emissions fell in 2011 for the third straight year, putting the state in a good position for meeting its target of reducing carbon emissions to 1990 levels by 2020, according to the California Air Resources Board (CARP) and as mandated by California AB32 (the Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006). Since businesses began reporting data in 2008, emissions have steadily declined from 133,4 million tons to 111million tons of carbon dioxide equivalent, shedding a full 22 percent in 2011.
Electricity production, once the leading sector for CO2 emissions in the state, made the biggest inroad towards reduction targets by cutting emissions 17.5 million ton between since 2008. Emissions from electricity generation was 34.9 million tons in 2011.
Renewables, conservation, carbon market contribute to reduction
Analysis from the CARB attributes the reduction in emissions from power generation to conservation and increased renewable energy production. California has one of the most ambitious renewable energy production targets in the US with a goal of 33 percent by 2020 through the California Renewables Portfolio Standard (RPS)
Last summer the California Public Utility Commission (CPUC) announced that the state was the first in the nation to install 1,000 megawatts of customer-generated solar power. Californiaís Independent System Operator (ISO) and the CPUC reported that on two occasions during August of last year a record-breaking 1,000 megawatts of solar energy was brought on line at one time, writes Noah Long in the Natural Resource Defense Fundís Switchboard. Thatís enough electricity to power the city of San Francisco or roughly as much power as is generated from two large gas plants. The stateís three largest electricity generators, Pacific Gas & Electric, Southern California Edison, and San Diego Gas & Electric, met intermediate RPS targets of 20 percent renewables for the period of 2011-2013 last summer as well.
With renewable energy production surging in the state, especially
solar, and its
carbon trading scheme now fully underway, California has an
excellent head start for meeting its emissions reduction and clean
energy production goals to help avoid the devastating effects of
climate change. Hopefully other states will follow.![]()